In the maintenance environment, one of the main concerns of managers and supervisors is the emergence of units that, due to their low performance, impact management from the shadows. These bad actors can be present in any type of maintenance, whether preventive, predictive, or reactive. However, it is in reactive maintenance where their negative impact on the business becomes most evident.
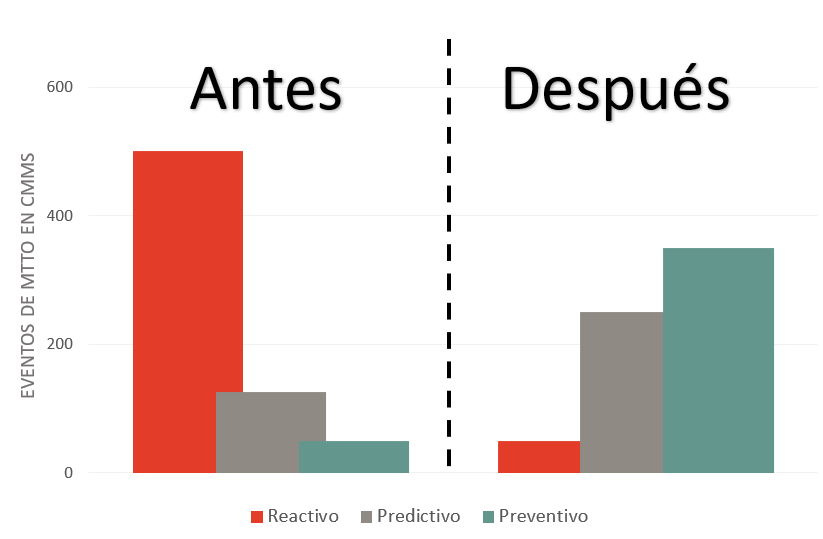
Changes in the type of maintenance applied before and after the implementation of MAO (Number of maintenance events recorded in the CMMS within a given period)
This is where the Hidden Bad Actors (MAO) methodology comes into play to effectively address this problem, evaluating statistics and the impact of maintenance activities in order to identify the units that present the greatest problems or a disproportionate impact on management. This is done through different approaches, such as impact on man-hours invested, maintenance budget, lost profits, reduction in reliability, safety, and quality, among other aspects.
Typically, the methodology consists of the following steps:

MAO Implementation Methodology
Assessment of the maintenance management and recording system
This first stage is key to properly understanding and feeding the artificial intelligence classification algorithms. Here, the classification instances that maintenance management has (as well as what the CMMS allows) are reviewed.
Categorization of records
All generated work orders are cataloged and reviewed using machine learning tools, systematically organizing the information and classifying it for analysis. The classification results in types of maintenance, nature, and required specialties.
Time, impact, and cost calculations
According to the information recorded in the CMMS, intermediate calculations are performed on each record and impacts are assigned. Costs can be calculated indirectly (man-hours, lost profits, quality, etc.) or may come directly from the CMMS source.
Statistical analysis
Statistical calculations of occurrence frequencies, averages, and deviations, among others, are carried out to search for insights that allow correcting present deviations.
Action plan
Based on the results of the previous step, an action plan is established to reduce the negative impact of these units’ performance on maintenance management.
The benefits of applying this methodology are diverse and highly effective. First, a high level of maturity in maintenance management is not required to implement it. In addition, it allows evaluating the impact of maintenance management from different approaches, which helps make more accurate decisions.
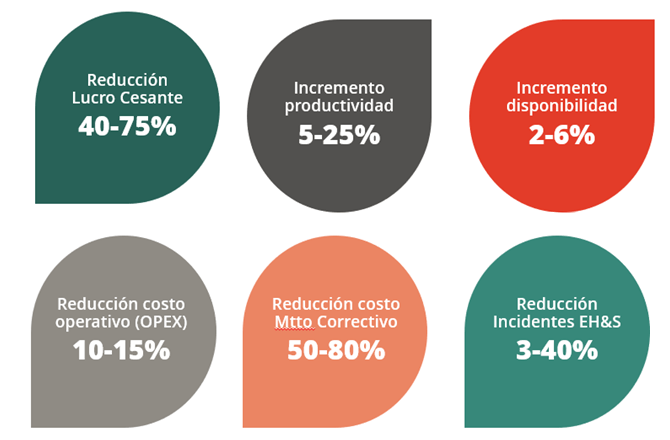
Benefits of MAO implementation
Another important benefit is that the results of the methodology can be managed automatically in monitoring dashboards supported by artificial intelligence. This allows greater efficiency in the process and better visualization of the results. In addition, the Hidden Bad Actors methodology helps reduce backlog activities and redirect management toward preventive and predictive activities.
In conclusion, the Hidden Bad Actors methodology is highly beneficial for maintenance management in any type of company. It helps identify problems that go unnoticed in day-to-day operations, make better decisions, and improve process efficiency. The methodology covers the first steps toward moving into planned management while promoting preventive and predictive practices.



















